In 2026, access to artificial intelligence is no longer a differentiator. Every sales professional has a ChatGPT login or a Copilot license. However, access doesn’t equal impact. A stark divide has emerged in the B2B landscape—not between those who have AI and those who don’t, but between those who dabble and those who integrate.
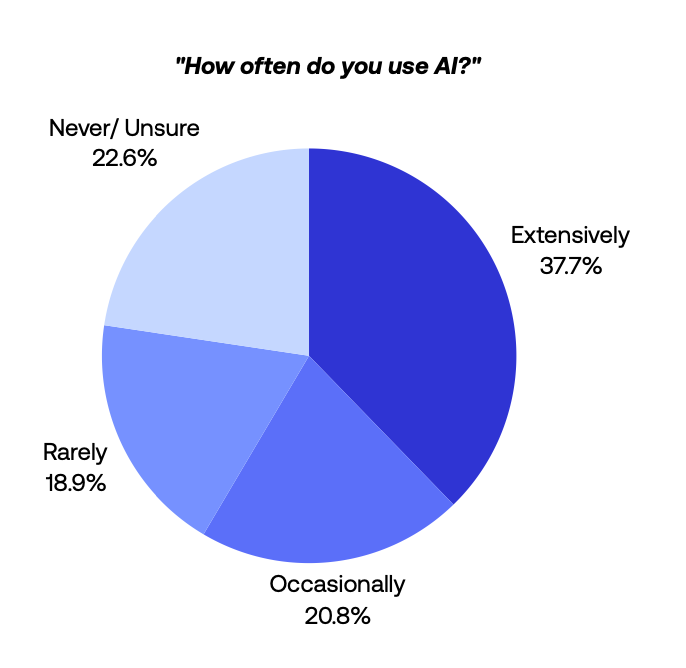
According to our State of Sales on LinkedIn for 2026 report, nearly 58% of sellers use AI in their workflow, yet only 37.7% use it extensively. The performance gap is real. Heavy AI users are 3.5 times more likely to book more than five meetings per month compared with sellers who rarely use AI.
We’ll show why dabbling slows reps down. Then we’ll map how teams use PhantomBuster to move from prompts to an automated workflow—clean data in, reviewed drafts out—so reps book more meetings in less time.
What does the “usage gap” in AI adoption look like?
Our survey of global sales professionals revealed that while 58% use AI in their LinkedIn workflow, usage patterns split into two distinct groups. The largest segment uses generative AI tools only occasionally—quick rewrites or idea generation rather than structured prospecting.
A smaller group—37.7% of respondents—uses AI daily as part of the workflow. For them, AI usage isn’t a task. It’s infrastructure that supports daily prospecting.
Group A: The extensive AI user
- Frequency: Uses AI consistently as part of their daily prospecting workflow
- Workflow: Message refinement, post creation, and summarizing prospect insights
- Result: 3.5 times more likely to book more than five meetings per month
- Common pattern: Runs automated profile extraction overnight, reviews AI-drafted messages each morning, personalizes top prospects before 10 AM
Group B: The occasional AI user
- Frequency: Uses AI when they “remember to,” or only for difficult messages
- Workflow: Manual copy-pasting into chatbots, limited prompts, inconsistent usage
- Result: Lower meeting generation; 83% spend more than five hours per week on LinkedIn due to workflow fragmentation
- Common failure mode: Opens ChatGPT, pastes a profile, waits for output, pastes back to LinkedIn—then repeats for the next lead, losing 3–5 minutes per cycle
In our interviews, top-performing teams integrate AI into a repeatable workflow rather than ad-hoc prompts. This works because daily use creates muscle memory around the steps, while occasional use forces reps to re-learn the process each time.
Why does occasional AI use break momentum?
The problem with occasional use is friction. If a sales rep has to stop what they’re doing, open a new tab, copy a LinkedIn profile, paste it into an LLM, write a prompt, and then paste the result back into an email, they save little time—often less than 1–2 minutes per lead—compared to manual research.
Our report shows that occasional AI users are actually the biggest time spenders, with 83% spending more than five hours per week on LinkedIn. Tool-switching adds 30–60 seconds per lead and interrupts review focus. Over a list of 50 leads, that’s 25–50 minutes lost to context-switching alone.
Occasional users also struggle with prompt quality. They treat large language models like a search bar, which produces generic outputs and weak personalization. In contrast, heavy users rely on AI to summarize prospect activity, refine messaging, and support contextual outreach, which helps them create more relevant conversations.
Occasional use breaks momentum. Daily, integrated use compounds results.
What daily workflow turns AI into booked meetings?
To move from Group B to Group A, you don’t need to work harder—you need consistent, AI-assisted workflows. This means shifting from one-off prompting to a structured system where AI supports repetitive tasks throughout the day.
Here’s a workflow top teams use to book more meetings with less manual work. The key is treating PhantomBuster as a connected system: extract profiles → auto-draft messages → human review → push to CRM—no tab-switching.
Step 1: Automate data gathering
Before you use generative AI, you need quality input. Manual research doesn’t scale past a few leads per day.
In PhantomBuster, the LinkedIn Profile Automation extracts About sections, recent posts, and company details automatically. Schedule it to run overnight or during lunch, and you’ll have structured prospect data waiting when you’re ready to draft.
This reduces research time from 5–7 minutes to 1–2 minutes per lead by auto-extracting profile context. You’re not cutting corners—you’re reallocating time from data entry to message strategy.
Step 2: Analyze profiles and draft messages with AI
This step turns profile context into draft messages tailored to each prospect. Instead of writing each message manually, you use the PhantomBuster AI LinkedIn Message Writer to process the extracted data.
The AI LinkedIn Message Writer analyzes the prospect’s profile, identifies pain points, and drafts messages that reference industry trends or mutual connections. Because it’s working from structured data PhantomBuster already extracted, you’re not re-entering context manually.
Personalize at volume: generate first drafts for every lead while keeping references to recent posts and company signals. This works because the AI has access to real profile activity, not just job titles.
Step 3: The human-in-the-loop review
Fully implemented AI doesn’t mean removing humans. It means letting humans focus on high-value decisions. Once drafts are ready, review for accuracy, tone, and compliance, then approve or edit.
Send approved drafts to your CRM (HubSpot, Salesforce, Pipedrive) via export or connector, keeping activity synced to records. This maintains consistent brand voice while eliminating the blank-page problem that slows manual workflows.
What changes when you automate AI workflows vs. running them manually?
The difference in sales performance becomes clearer when paired with data. In our report, automation-heavy teams are the most likely to exceed five meetings per month, and extensive AI users are 3.5 times more likely to reach that benchmark than those who rarely use AI.
Manual steps add minutes per lead across research, prompting, and copy-pasting. In our report, 52% send fewer than 10 DMs per week due to time lost to research, prompting, and copy-pasting.
Here’s how the two approaches compare at an operational level:
| Metric | Occasional AI User (Manual) | Extensive AI User (PhantomBuster) |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Output | 8–10 messages reviewed/hour due to manual switching | 20–25 messages reviewed/hour through automation |
| Research Depth | Surface level, mostly job titles | Deep insights from extracted posts, recent activity, and company signals |
| Message Quality | Generic or lightly personalized | Context-rich, AI-drafted messages (e.g., reference a post from last week + company hiring signal) |
| Time per Lead | 6–8 minutes because every step is manual | 1–2 minutes because AI prepares drafts for human review |
| Meeting Outcomes | 67% book 5 or fewer meetings per month | 45% likelihood of exceeding 5 meetings per month |
Automation reallocates time toward higher-impact work. Sales teams that adopt these workflows see more consistent pipeline generation, stronger personalization, and fewer lost opportunities.
What keeps teams from consistent implementation—and how to remove it?
Many teams acknowledge the benefits of AI but hesitate to implement it consistently. The report highlights two main barriers:
- Concerns about data security
- Lack of technical confidence within sales teams
These issues slow adoption even when the underlying workflows are simple.
PhantomBuster runs in the cloud with scheduled runs and rate-limit controls, so workflows stay consistent as volume grows. Cloud runs keep schedules reliable, so reps start each day with fresh context and ready-to-review drafts.
A human review loop helps maintain accuracy and brand voice while reducing the risk of off-target messages. Across responses in our survey, teams that already document workflows see greater gains from AI. This works because AI amplifies existing structure rather than creating it from scratch.
To avoid fragmented usage, sales operations leaders should introduce shared workflows and clear ownership. Teams that adopt AI consistently see more predictable output and fewer slowdowns from manual steps.
What should sales teams expect from AI agents next?
Like driver-assist moving toward autonomous, sales workflows are shifting from AI-assisted to AI-orchestrated tasks. In sales, agent-like workflows can chain steps—find lead → extract profile → draft message. PhantomBuster supports this via connected automations and scheduled runs with human approval before send.
We’re already seeing emerging trends where speech recognition and voice AI will handle customer interactions. But for B2B sales in 2026, the main opportunity lies in text-based content creation and outreach strategies.
Teams that use AI daily build compounding gains—more reviewed messages and more meetings per rep. They’re not just using tools; they’re building systems that fundamentally reshape how prospecting gets done.
What to do next: move from ad-hoc prompts to a daily workflow
The data is clear. Occasional use produces inconsistent results, while consistent use creates stable workflows that support better personalization and more reliable performance. In our report, 67% of sellers still book five or fewer meetings per month, which shows how much room there is for improvement.
Teams that treat AI as infrastructure, not an occasional shortcut, see more predictable outcomes. PhantomBuster helps automate the research and drafting stages so sellers can move from irregular prompting to a structured, scalable prospecting system.
Most organizations are still formalizing their approach to AI. This creates an opportunity for teams that adopt consistent, workflow-based usage to build meaningful operational advantages in 2026.
FAQ: How should sales teams use AI daily?
What do the AI sales statistics say about daily usage?
Our research indicates a strong correlation between frequency of use and success. Extensive users of AI tools are 3.5 times more likely to book more than five meetings per month compared with occasional users. This is because daily users integrate AI into their core workflow, automating routine tasks like research and drafting, whereas occasional users struggle with context-switching and lack data-driven insights.
How does PhantomBuster help me become a daily user?
PhantomBuster removes the busy work: it extracts LinkedIn profile data in the cloud, sends it to the AI LinkedIn Message Writer, and returns reviewed drafts to your CRM. This lets you apply AI drafting across your entire lead list without adding manual entry time.
Are there data security risks with using AI tools?
Yes, if you use the wrong tools. Some extensions may store data locally or operate outside platform policies. Prefer cloud workflows with permission controls and documented rate limits.
PhantomBuster runs in the cloud and supports permissioned access, scheduled runs, and rate-limit settings to reduce operational risk. We also recommend a human-in-the-loop workflow, ensuring that all customer interactions are reviewed by a human before sending, maintaining data governance.
Will implementing AI replace sales representatives?
No. The goal of implementing AI is to replace the tasks of a sales rep (data entry, research, drafting), not the role. Human intelligence is still required to close deals, build relationships, and interpret complex customer experiences. AI handles the sales operations and lead generation, freeing up humans to focus on high-value conversations.
What is “agentic AI” in the context of sales?
In sales, agent-like workflows can chain steps—find lead → extract profile → draft message. PhantomBuster supports this via connected automations and scheduled runs with human approval before send. The key difference from standalone AI tools is that each step feeds directly into the next without manual intervention.
How does AI impact customer satisfaction?
Personalized first touches that reference recent posts tend to earn more replies than generic blasts. Use AI LinkedIn Message Writer prompts that cite 1–2 verifiable details (a recent post, a company announcement, or a shared connection). This nuanced understanding leads to better first impressions and more meaningful connections.
